Green Logistics for Greener Supply Chain Management

by
Alisa Cvilij
May 29, 2024
Every industry's environmental impact is in the public eye. Logistics and transportation companies are under scrutiny more than the rest. Thus, green logistics is something that companies and vehicle manufacturers are looking into nowadays.
Governments worldwide are regulating emissions, waste management, and fuel efficiency. Customers and investors opt to deal with companies that adhere to these regulations, placing pressure upon logistics companies to adopt sustainable practices.
The green logistics market was valued at USD 1.3 trillion in 2022. Predictions put this figure at USD 2.47 trillion by 2030, a CAGR of 8.35 percent between 2023 and 2030.
Companies and customers are aware of things like carbon emissions, sustainable packaging, and biofuel, to name a few. As a result, logistics activities, particularly shipments, are becoming eco-friendlier. To reduce environmental impact, logistics industries embrace sustainable practices. Those could include eco-packaging, electric trucks, alternative fuel, and more.
Keep reading to explore green logistics. We will dive into environmentally and eco-friendly distribution and supply chain management.
Table of contents
1. What is green logistics?
2. What is a green supply chain?
3. Green logistics strategies for greener transportation
What is green logistics?
First, let's define the term green logistics.
Thus, what is green logistics?
Green Logistics are: Systems and practices implemented in the transportation and logistics industry to promote sustainability. This involves reducing carbon emissions and implementing environmentally-friendly solutions to industry challenges.
In their quest to reduce their carbon footprint, logistic companies have implemented different strategies. Below are some green logistics examples that are being embraced by global supply chains.

- Sustainable packaging
- Alternative fuels that are derived from sources other than petroleum
- Electric trucks
- Optimization of operations and workflows with the aid of technology
With the goal of
- Reduced carbon emissions
- Improved air and water quality
Green logistics strategies can be applied to all types of industry processes. Examples include inbound and outbound logistics. Reverse logistics for returns and recycling, and many other business operations. It is important that green logistics serve the environment instead of working against it.
Eco logistics still needs to make sense costs-wise. That is important not only for the environment but also for the companies making the environmental transition. Also, companies must still maintain their customer satisfaction levels.
The global trend in the logistics sector involves the following practices:
- Consciousness of energy consumption;
- Packaging;
- Air quality;
- and the impact of business activities on the environment.
Also, logistics costs are always considered in the context of a greater environment, i.e., supply chains. Let's take a closer look.
What is a green supply chain?
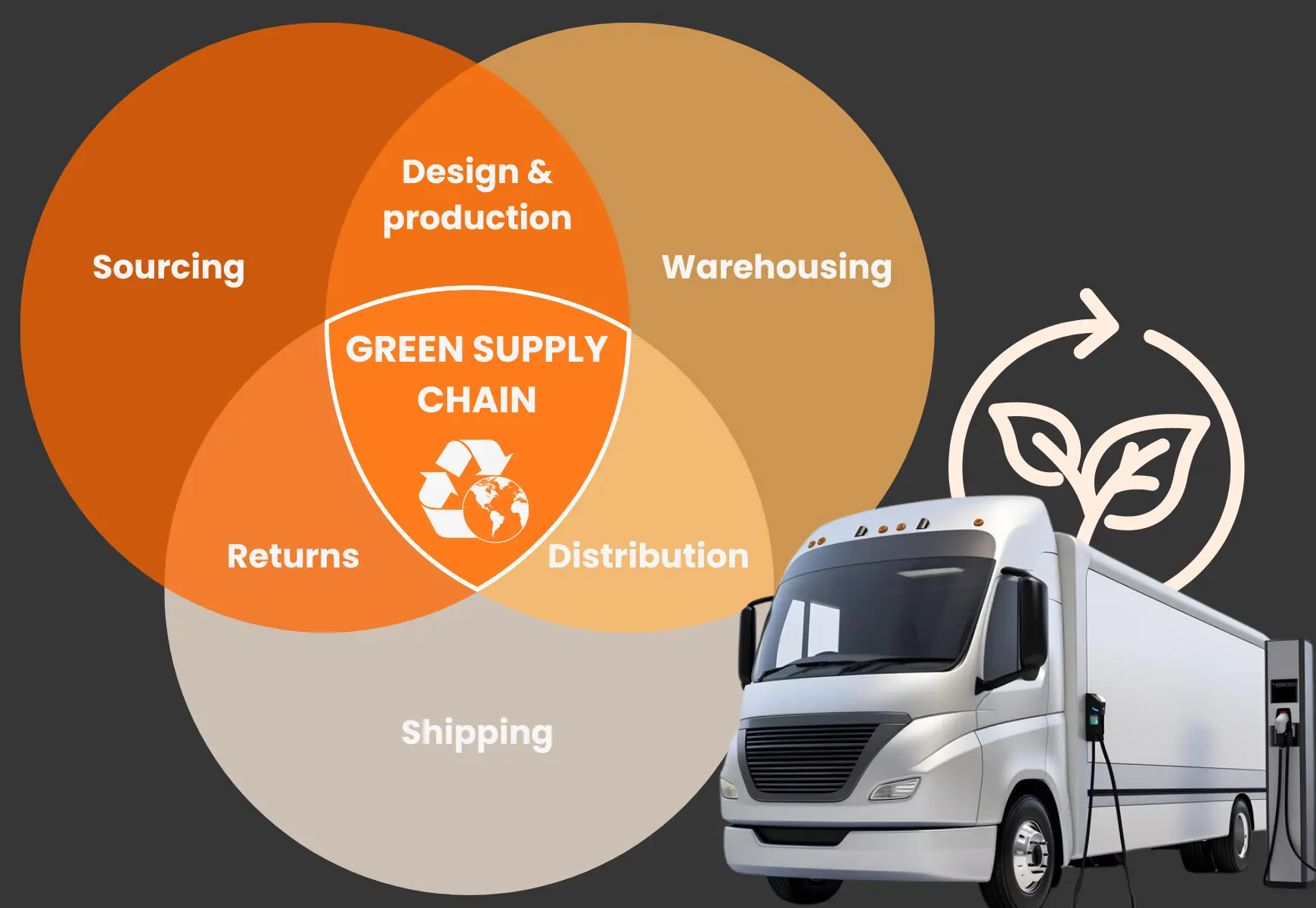
Green logistics strategies are but a portion of the larger supply chain system. The performance measurement for green supply chain management strategies include sustainability in:
- sourcing of materials
- product design
- production
- warehousing
- distribution.
Collaboration between the various supply chain managers is necessary. This will help to ensure compliance with these standards. Documentation of guidelines, benchmarks and goals need to be shared between the key stakeholders.
Let’s take a look at the green strategies for supply chain management. What they entail, what are the methods and technology needed to make the transition?
In this chapter of the green supply chain strategies:
1. Sourcing
2. Design
3. Production
4. Warehousing
5. Distribution
6. Shipments
7. Returns
Sourcing
What does green sourcing mean? That raw materials sourced for manufacturing and production are obtained from environmentally friendly sources. And with the least energy consumption and waste.
Ideally, green sourcing has the smallest environmental impact. It entails no greenhouse gas emissions and uses renewable energy. Eco-sourcing is crucial for green production and is key to building a green business.
Design
Let's explore green or sustainable design. This approach involves designing products that produce less waste without sacrificing efficiency.
The green design could involve the production of consumer goods using locally sourced sustainable materials. E.g., designing buildings with large windows for light, false ceilings for noise control, and solar panels for the production of power.
Production
Green production is the type of production that uses the least energy and produces minimum to zero emissions. This means using local and renewable resources where possible and reducing waste. It involves investment in waste management and recycling solutions.
Green production relies on infrastructure and technology that help reduce the carbon footprint. Moreover, they support green supply chain systems and strategies.
Warehousing
Green warehousing is about integrating warehousing practices with sustainable facilities and activities. Examples of this are:
- Solar panels and solar lighting.
- Electric forklift equipment.
- Eco-friendly packaging.
- Minimizing paperwork with the aid of technology.
Following digital technology in warehousing. Inventory and warehouse management systems (WMS) help companies to optimize their stock levels. This reduces the need for extra warehouse space. It also helps to optimize warehouse operations, thus improving the carbon footprint.
Companies that build sustainable warehouses are future-proofing their entire production and distribution processes. They will be ahead of their sector when green practices become mandatory.
Distribution
What is green distribution in a supply chain context? It is an eco-friendly manufacturer and distributor of products from the beginning of the product journey to the end customer. Companies that are reducing their logistics carbon footprint look for supply chain partners. Those supply chain partners should have similar environmental strategies.
Freight and delivery companies use route planning and route optimization systems. This helps to improve logistics efficiency. Route planner tools help keep delivery costs low while also minimizing fuel consumption. Additionally, route planners help to optimize load, and keep customers happy with features like track and trace.
Last-mile delivery solutions like Track-POD, offer full-spectrum green transportation solutions to logistics challenges. They include reverse logistics. Check Track-POD's software's usage case study with zero-emissions business ZMOVE. Zero-emission businesses like that improve air quality by offering deliveries without carbon emissions.

Shipments
Shipments, or freight logistics, refer to the transportation of goods across land, air, and sea. Green transportation in supply chain management must have sustainability as a priority. This means making attempts to reduce the burning of fossil fuels, reduce their emissions, and pollution.
Returns
A major part of sustainable logistics and supply chains is reverse logistics. Reverse logistics means returning goods for recycling or repair. A reverse logistics strategy helps companies process returns and support product recycling, which reduces waste and promotes sustainability. Route planning systems can plan returns as part of the delivery schedule, saving unnecessary trips, fuel, and time.
It's important that reverse logistics solutions are built around the customer, as the customer is also a point of contact in the supply chain. Customers need transparent and efficient processes, which will allow them to participate in waste reduction strategies.
Green logistics strategies for greener transportation
Further, let's explore the transportation strategies that promote sustainability.
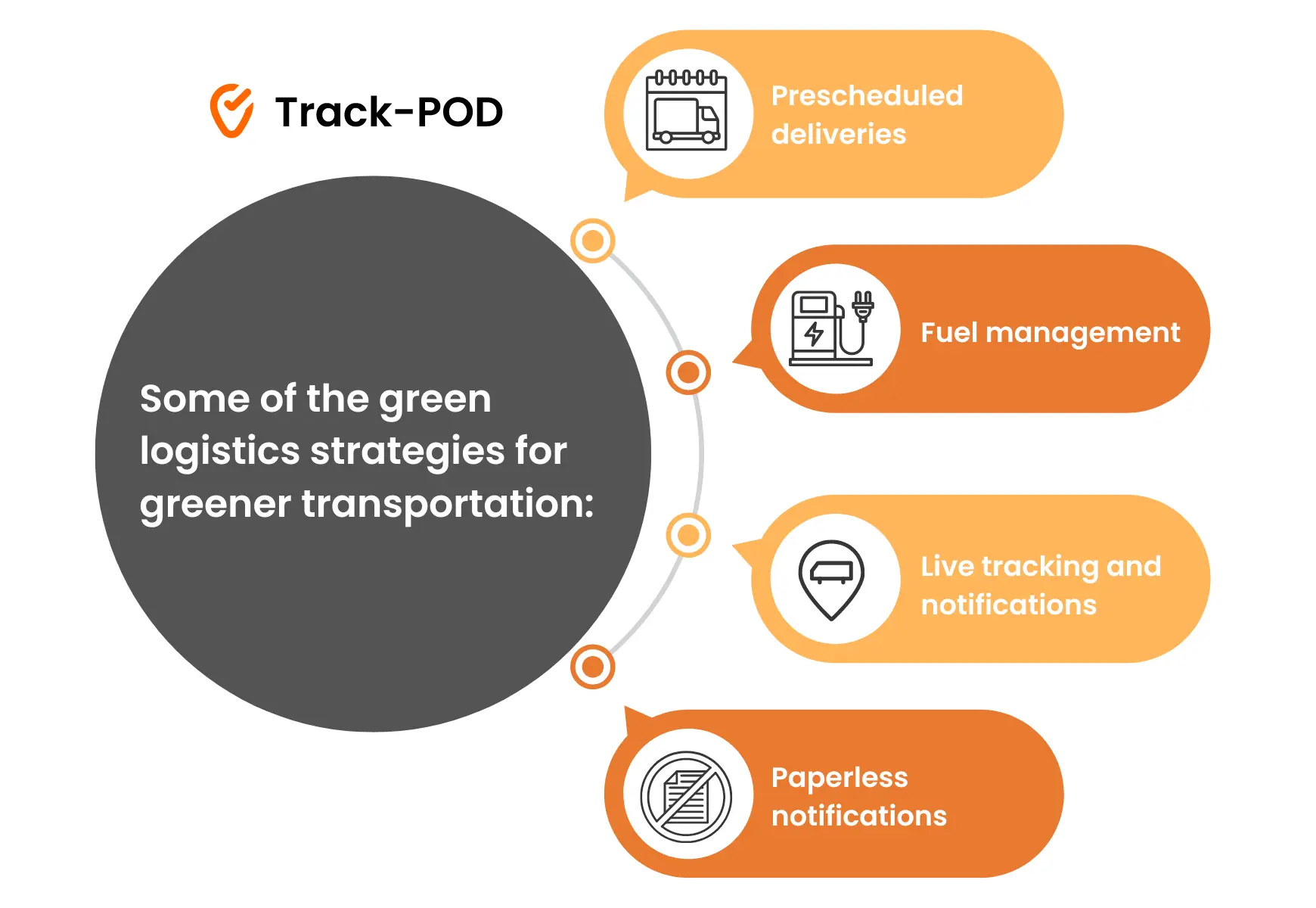
Prescheduled deliveries
Prescheduled deliveries are a great example of how timely planning can reduce greenhouse gas emissions in logistics. They are opposites of on-demand deliveries. When you plan shipments, you create more efficient routes. That can be done by combining local dropoff/pickup points for the greatest efficiency.
Prescheduled deliveries contribute to more efficient use of transport. Moreover, they help you control the environmental impact of your logistics operations. Logistics managers can plan multi-drop routes using route planning software, which can also help cut delivery costs.
Read on: Uber Eats lesson for food delivery businesses [prescheduled delivery].
Fuel management
Fleet management and fuel management in particular are used by logistics and freight operations to reduce fuel costs. Or some companies have moved to biofuel altogether.
Fleet management can involve load checks and fleet optimization, depending on vehicle capacity. Moreover, it can include safety checks, i.e. proactive vehicle maintenance, to ensure safety for your drivers and customers.

Live tracking & notifications
Live tracking and notifications for customers have a lot of benefits.
- You cut your customer support costs by automating the process of providing shipping updates.
By sharing a live tracking link with your consumers and an estimated time of arrival (ETA). This helps you to increase your rate of successful deliveries by making sure the customers will be home for their delivery. In addition to cost-cutting benefits for the company, you get environmental benefits. Your drivers don't need to make multiple trips to the same delivery point twice if the customers are at home for their delivery.
Paperless operations
The logistics industry is going paperless. And there's a good reason for that. Companies that care about environmental impact and efficiency are digitalizing their business processes. That extends to logistics and freight documentation.
Back in the day, Proof of Delivery was a paper document that the customer needed to sign for the business to be considered concluded. Nowadays, any logistics business can move to paperless and contactless delivery. That can be done using electronic signatures and photo proof, which can be easily collected through driver apps. Check Track-POD's driver app, for example.
Build your green logistics strategy with Track-POD
Track-POD is a transportation management system (TMS). It supports green logistics processes with technological backup. This involves route optimization for different vehicle types. (Including cargo bikes and electric cars.) Another feature is paperless Proof of Delivery. Make sure to try Track-POD for your green logistics process.

Are you ready to reduce your company's environmental impact by using sustainable logistical solutions? Book a free demo, and let's discuss eco logistics.
- Transportation management
About The Author
Alisa Cvilij
Content Marketer at Track-POD. Passionate about building meaningful and helpful content for the readers.